Author- Akash Roy, Technical Consultant (DevOps)
Lately there have been a lot of buzz about a new service offered by Microsoft as a part of Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS). There are several important differences between Windows 365 and Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD)
In this article we will be discussing about the similarities as well as the differences between both Windows 365 service and Azure Virtual Desktop Service along with its offerings. These comparisons will be on several factors in detail.
We shall investigate these 2 services based on 5 primary Areas; they are:
- The architecture of the Services
- Experience of the IT Admin
- Experience of the end-user
- Infrastructure and Licensing
- Costing based on consumption
Technical Architecture
Before Proceeding with the similarities and differences let us first understand what Windows 365 is.
Windows 365 is a new service that helps business customers to access Cloud PCs from anywhere across the globe and access it using any device (Laptop, Tablet, MacBook, iPhone, Android etc)
With respect to the architecture, W365 is based on top of the AVD architecture itself. The only difference is the transactional model i.e.: Fixed price or Transactional based
Windows 365 has 2 versions of Cloud PCs. There are 2 versions of cloud PCs
- Enterprise
- Business
Enterprise Cloud PCs
Enterprise cloud PCs are designed for organizations that have invested in Microsoft Endpoint Manager and are using this powerful platform to manage their existing, physical Windows 10 desktops.
Enterprise cloud PC requires an Intune license for each user who is assigned an M365 SKU PC
Enterprise Cloud PC Architecture
In order to deploy an Enterprise Cloud PC in an organization, you would require an Azure subscription with a properly configured network with access to Active Directory. The Active Directory should have Azure AD Hybrid Join enabled.
Enterprise Cloud PC does not support Azure AD DS and cloud-only, Azure AD join as of creating the document but might support in the future.
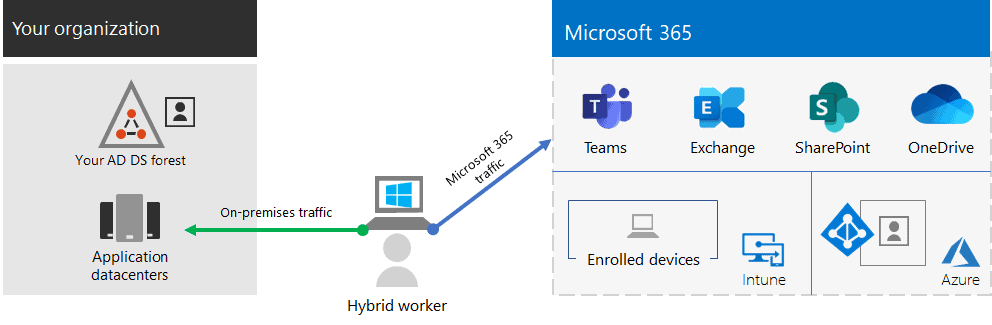
In Windows 365, The compute services such as Virtual Machine, Virtual Network and so on will be managed by Microsoft. The VM itself runs in a Microsoft-managed Azure subscription, hence admins don’t have access to it directly and are not incurring the cost of this VM in their own Azure subscription. The cost of the VM is incurred by Microsoft where the Windows 365 is hosted, Although the VMs NIC will be injected in the customer’s Azure Subscription and the customer will incur the charge for the same.
All the traffic enters and leaves the Windows 365 via the customer managed VNET. The customer will handle the Egress cost and will be charged. Hence the customer will be paying the Egress cost.
Since admins don’t have direct access to the VM running in Microsoft’s Azure subscription, all management tasks such as software installation, Patching, Policies and so on will be performed through the Microsoft Endpoint Manager portal.
Enterprise cloud PC pre-requisites:
In order to set up an Enterprise Cloud PC, there are certain prerequisites that need to be followed. These Pre-requisites are:
- Azure subscription with Vnet: Since most of the compute services are managed by Microsoft themselves, the only deployment in a customer’s environment would be the Virtual Network. Hence, an Azure subscription with a Virtual Network would be required from the customer’s end.
- Azure Vnet can access the Active Directory domain controller (i.e. a PC can be joined to the domain). Custom DNS servers, necessary routing, and firewall access to AD.
- Azure AD Connect should be configured and should be running within Active Directory with AAD Hybrid Join enabled.
- Intune must be enabled on the Azure AD tenant since each cloud PC user should have an Intune license assigned to him/her.
- The admin who shall be setting up the initial deployment must be the owner of the Azure subscription where Enterprise Cloud PC will be deployed
- Azure AD DS is NOT supported as of now.
Business Cloud PCs
Business cloud PCs are designed for individual users and very small businesses who are restricted with their budgets and need to have a virtual desktop.
Now, instead of purchasing a basic laptop, they can go to Microsoft and subscribe to a new cloud PC and have it ready to use in an hour
Business cloud PCs do not require an Intune license and are managed entirely by the user, similar to a standalone physical PC hence providing the best of both the worlds.
Business Cloud PC Architecture
Business cloud PCs are VMs that run entirely in Microsoft’s Azure subscription, including the network interface cards. The customer does not need to provide an Azure subscription. There is no Active Directory dependency since Business cloud PCs natively join Azure AD. Unlike Enterprise Cloud PCs, there is also no requirement of an Intune license as well.
Business cloud PCs route all traffic through Microsoft-controlled network infrastructure and there is no way for admins to control the inbound or outbound connectivity to/from these VMs
There is currently no way to assign static IPs to Business cloud PCs.
Since these cloud PCs run in Azure subscription of Microsoft and since they are not enrolled in Intune, there is no admin interface to manage the service by the Admin. They can be managed directly by the user, similar to a standalone physical Windows device.
There are no pre-requisites and no setup steps needed for Business cloud PCs. The admin has to assign a Business cloud PC license to a user in the Windows 365 Admin portal and the new desktop gets provisioned within an hour.
Now that we have learned a little about what Windows 365 is, we shall now look at the comparison points between Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) and Windows 365 (W365).
You can take a look at the difference from the documentation, AVD vs W365- Architecture.












